AI Dependency Erodes Critical Thinking: Brain Scans Show Cognitive Decline in ChatGPT Users
Study Warns: Over-Reliance on ChatGPT May Harm Learning Abilities
A groundbreaking MIT Media Lab study reveals that frequent use of AI tools like ChatGPT could impair memory, critical thinking, and creativity in students. The research tracked 54 students during essay-writing tasks, comparing those using ChatGPT, Google, and no external help. Findings showed concerning declines in cognitive engagement among AI users.

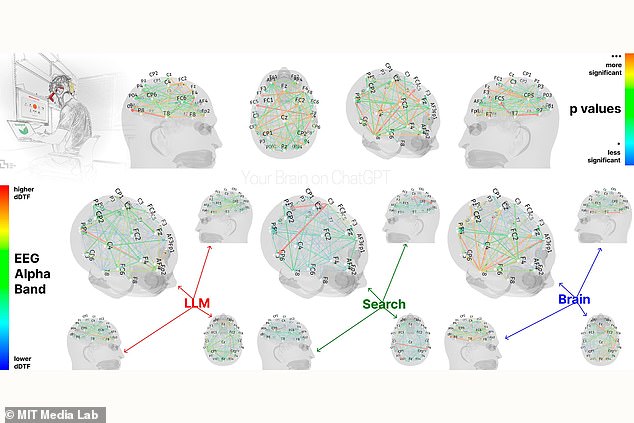
Students using ChatGPT showed reduced brain activity compared to groups using Google or no tools.
The Experiment
Participants were divided into three groups:
- ChatGPT (LLM): Accessed AI for essay writing.
- Google: Researched using the search engine.
- Brain-only: No external tools allowed.
All wore EEG devices to measure brain activity. Over four months, the ChatGPT group consistently underperformed in neural engagement, linguistic originality, and essay scores. Researchers noted their dependency on AI led to poorer memory retention and reduced critical analysis.
Key Findings
- Cognitive Decline: ChatGPT users exhibited weaker brain activity, suggesting diminished effort in synthesizing ideas.
- Google Group: Showed moderate engagement, blending external research with personal input.
- Brain-only Group: Demonstrated the highest neural activity and creativity, relying solely on existing knowledge.

Students without AI assistance produced more original content with heightened brain activity.
The Hidden Cost of Convenience
While ChatGPT offered faster solutions, researchers warned of an “echo chamber” effect. Users often accepted AI outputs without scrutiny, potentially adopting biases embedded in training data. “The convenience comes at a cognitive cost,” the study noted, highlighting reduced motivation to verify information.
When ChatGPT users later attempted essays without AI, their brain activity briefly increased as they struggled to integrate prior knowledge. In contrast, the AI-dependent group’s performance remained lackluster even when writing independently.
Implications for Education
The study emphasizes balancing AI use with active learning. Lead researchers caution: “Over-reliance risks eroding foundational skills like critical thinking and problem-solving.” Educators are urged to design AI policies that prioritize skill development over shortcuts.

Overuse of AI tools may lead to long-term cognitive trade-offs.
Conclusion
While ChatGPT streamlines tasks, the MIT study underscores the importance of mindful usage. As AI becomes ubiquitous, fostering self-reliance and analytical skills remains crucial for sustaining intellectual growth. The challenge lies in leveraging technology without compromising cognitive vitality.
Word count: ~600