Earth’s Annual Climate Cycle Expands: Scientists Identify Two New Seasonal Phases
Haze and Trash Seasons: Humanity’s New Climate Norm
Experts warn that human activities have introduced destructive new “seasons” to Earth’s climate calendar. Annual haze and trash events now disrupt ecosystems, endanger health, and redefine traditional seasonal patterns.
The Emergence of Haze Season
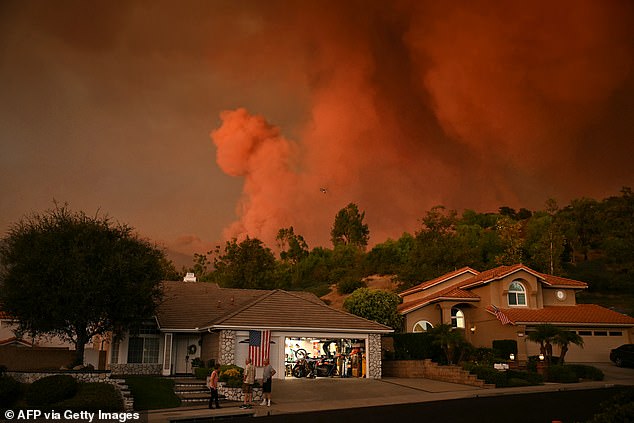
Haze season has become a perilous fixture in regions like Southeast Asia and the western U.S. In Indonesia and Malaysia, agricultural fires used to clear land create toxic smoke blankets from June to September, choking cities like Singapore and Kuala Lumpur. Similarly, California’s wildfire season—once confined to summer—now starts in spring and lingers into December. In 2023, Canadian wildfires shrouded New York and the U.S. East Coast in apocalyptic orange skies, signaling a recurring “smoke season.”
Image: Thick wildfire smoke engulfing California, highlighting the extended fire season.
Trash Season’s Plastic Tide
Bali faces a different crisis: “trash season.” From December to March, monsoons drive ocean currents to dump tons of plastic waste onto beaches. In 2024, over 3,000 tons of debris washed ashore, requiring armies of cleaners. Similar patterns plague Thailand, the Philippines, and even the U.S. East Coast, where summer currents funnel garbage into Florida and the Carolinas.
Image: Volunteers clearing plastic waste on a Bali beach during monsoon-driven trash season.
Vanishing and Shifting Seasons
Climate change isn’t just creating new seasons—it’s erasing old ones. Alpine regions like the Rockies and Andes face “extinct” winters as snowpack dwindles, devastating ski industries and ecosystems. In northeast England, seabird breeding cycles have disintegrated, severing a centuries-old ecological rhythm.
Image: A snowless Andes mountain range, illustrating vanishing winters.
Seasons Out of Sync
“Arrhythmic seasons” describe disrupted natural cycles. European spring now arrives weeks early, mismatching plant blooming and animal hibernation. North America’s wildfire and hurricane seasons last longer, complicating disaster preparedness. Meanwhile, summers in Europe have intensified into lethal “syncopated seasons.” Since the deadly 2003 heatwave killed thousands, heat-related deaths have surged, with summers following the same timeline but delivering unprecedented extremes.
A Call for Global Awareness
Researchers from the London School of Economics stress that these human-driven patterns demand urgent action. From Bali’s plastic tides to New York’s smoky skies, the planet’s new rhythm underscores the need for sustainable practices and policy reforms. As traditional climates fracture, adapting to these “seasons” may define humanity’s future resilience.
Image: New York City’s skyline obscured by wildfire smoke, a sign of recurring air quality crises.
Word count: ~600