Top Four U.S. Psychopath Hotspots: Could Your State Be Among Them?
Study Reveals U.S. States with Highest ‘Dark’ Personality Traits
Scientists have identified U.S. states where residents are more likely to exhibit “dark” personality traits, including narcissism, Machiavellianism, psychopathy, and sadism. The study, led by researchers at the University of Copenhagen, analyzed data from 144,576 Americans collected between 2019 and 2024.
High-Scoring States
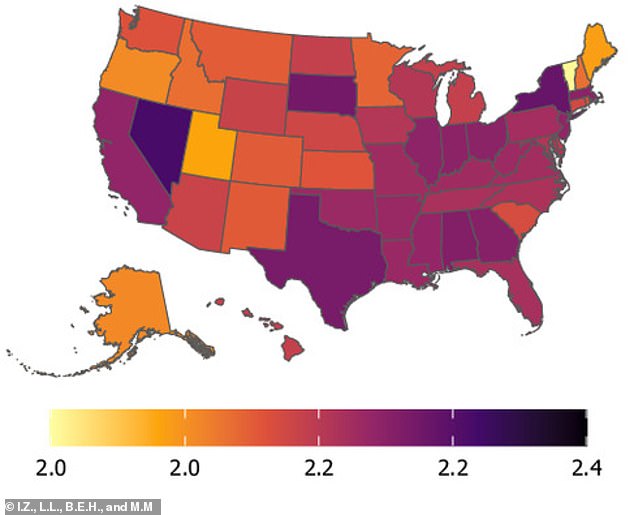
Nevada, Louisiana, New York, and Texas ranked highest for these traits. Nevada’s gambling culture and ties to risky behavior may explain its top spot, while Louisiana battles high homicide rates and economic challenges. New York and Texas were linked to stark wealth gaps, where extreme poverty exists alongside affluence. Other states with elevated scores included Alabama, Mississippi, and California. The latter, known for its tech and entertainment wealth, also faces significant income inequality, homelessness, and urban crime.
[Image: Nevada’s Las Vegas skyline, with caption: Nevada’s gambling culture may drive higher levels of risky behavior and dark personality traits.]
Societal Conditions Matter
Researchers connected these traits to adverse societal conditions (ASC), such as poverty, corruption, violence, and poor healthcare. They created an ASC index using Census Bureau data on inequality, poverty, homicide rates, and corruption convictions. States like Louisiana and Mississippi, which struggle with crime and limited resources, scored highly, reinforcing the idea that harsh environments may foster manipulative or aggressive behaviors.
Lowest Dark Trait States
Vermont, Massachusetts, New York (for certain regions), and Maine scored lowest. These states typically have stronger social services, education, healthcare, and economic stability, suggesting better community support reduces the prevalence of dark traits.
[Image: Vermont’s rural landscape, with caption: Vermont’s strong social services and education contribute to lower levels of dark personality traits.]
Methodology and Findings
Participants completed surveys measuring the “Dark Factor of Personality” (D), which assesses tendencies toward exploitation and selfishness. The study found a small but significant link between a state’s ASC score and its average D score. For example, Alaska and Rocky Mountain states like Oregon scored lower—potentially due to cultural emphasis on resilience and community cooperation.
Long-Term Implications
Notably, societal conditions impacted personality traits even 20 years later, implying that environments shape behavior over time. “Aversive traits like aggression or exploitation carry high social costs,” said lead author Ingo Zettler. “Even minor differences can profoundly affect how societies function.” The team believes these findings highlight the need for policies addressing inequality and improving community resources.
[Image: Chart comparing state ASC and D scores, with caption: Higher poverty and crime correlate with elevated dark trait scores.]
Conclusion
While genetics and other factors play a role, the study underscores how societal conditions can amplify harmful traits. Reducing poverty, improving healthcare, and fostering equity, researchers argue, could create healthier communities—and personalities.
Adapted from a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.